Monitoring TrilioVault for Kubernetes Resources with BotKube

Introduction
In today’s fast-paced environment, it’s more important than ever to simplify backup management. Trilio is ready to help by providing an easy way to receive notifications from your Kubernetes applications in your communication tools of choice. This includes Slack, one of the fastest-growing communication tools in use today. In order to provide a more consistent user experience across ecosystem tools, you can set up support for TVK resource notifications in Slack through BotKube. This way users can view all of their notifications in the same communication tool that they are already using, saving time and effort.
This guide provides detailed instructions for how to install BotKube on a Kubernetes cluster, configure it to integrate with Slack and monitor TVK resources via notifications within Slack channels.
What is TrilioVault for Kubernetes?
TrilioVault for Kubernetes is a trusted cloud-native data protection platform specifically designed to protect Kubernetes-based applications across multiple cloud environments. It provides application-centric backup, allowing you to backup and restore all data, metadata and Kubernetes objects associated with the application. TrilioVault provides insight into and discovery of Kubernetes applications while allowing you to run backup operations across namespace, label, Helm and Operator-based applications. Since metadata is vital to everything from container orchestration to managing applications, TrilioVault stores data and metadata together, making them simple to manage.
What is BotKube and Why Should You Use It?
BotKube is a messaging bot for monitoring and debugging Kubernetes clusters. It can be integrated with multiple messaging platforms, like Slack, Mattermost, Microsoft Teams, Discord and more, to help you monitor TVK/Kubernetes resources.
Install and Configure TVK
Here are the detailed steps to install and configure TVK. Along with TVK, the user needs to configure a few resources before they can start the backup. Begin by learning how to get started with TVK and how to install TrilioVault for Kubernetes.
Install and Configure BotKube with Slack
Install BotKube App in Slack Workspace
Search for the BotKube application in the Apps section on Slack and install the application using the Add to Slack button provided. After you authorize the application, you will get a BOT Access token. Take note of this token as it will be required during the deployment of the BotKube backend on the Kubernetes cluster.
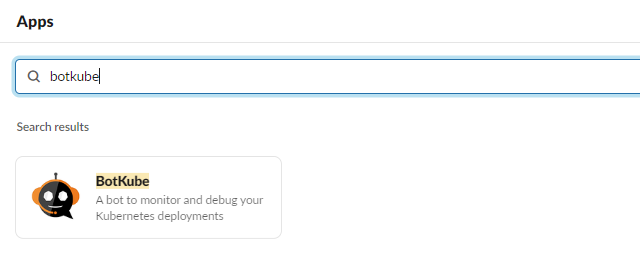
Follow the steps below to install and configure BotKube with TrilioVault for Kubernetes and Slack in order to receive all of your notifications about changes happening on the Kubernetes cluster in one place.
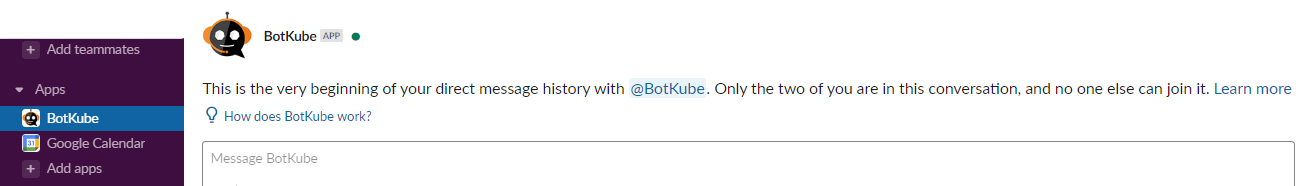
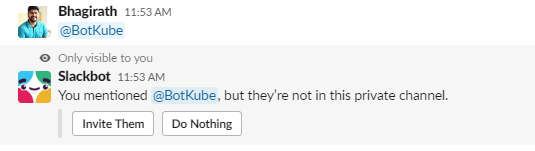
Add BotKube App as a User on Slack Channel
Once the BotKube application is installed in the Slack workspace, you’ll see the BotKube user handle (@Botkube). Add the BotKube user to the slack channel from which you want to monitor the TVK resources.
Install BotKube Backend in the Kubernetes Cluster
-
Add infracloudio chart repository to the Kubernetes cluster.
helm repo add infracloudio https://infracloudio.github.io/charts helm repo update -
Install BotKube backend with the required input parameters to configure Slack communication.
helm install --version v0.12.1 botkube --namespace botkube \ --set communications.slack.enabled=true \ --set communications.slack.channel=<SLACK_CHANNEL_NAME> \ --set communications.slack.token=<xoxb-SLACK_API_TOKEN_FOR_THE_BOT> \ --set config.settings.clustername=<K8S_CLUSTER_NAME> \ --set config.settings.kubectl.enabled=<ALLOW_KUBECTL_true_or_false>\ --set image.repository=infracloudio/botkube \ --set image.tag=v0.12.1 \ infracloudio/botkube -
Verify that the BotKube controller pod is in a running state.
kubectl get pod -n botkube NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE botkube-6fdf477b-gskb7 1/1 Running 9 12d
Note: After the above installation with the default configuration, BotKube will watch all the resources in all the namespaces for create, delete and error events in the configured Kubernetes cluster.
Configure TrilioVault for Kubernetes Resource Monitoring
-
Along with default configurations, update the botkube-configmap with TVK custom resources for monitoring.
kubectl get configmap -n botkube NAME DATA AGE botkube-configmap 1 14d kube-root-ca.crt 1 15d -
Add TVK custom resources to the BotKube configmap.
kubectl edit configmap botkube-configmap -n botkubeapiVersion: v1 data: resource_config.yaml: | recommendations: true resources: - events: - all name: triliovault.trilio.io/v1/licenses namespaces: ignore: - null include: - all - events: - all name: triliovault.trilio.io/v1/targets namespaces: ignore: - null include: - all - events: - all name: triliovault.trilio.io/v1/policies namespaces: ignore: - null include: - all - events: - all name: triliovault.trilio.io/v1/hooks namespaces: ignore: - null include: - all - events: - all name: triliovault.trilio.io/v1/backupplans namespaces: ignore: - null include: - all - events: - all name: triliovault.trilio.io/v1/backups namespaces: ignore: - null include: - all - events: - all name: triliovault.trilio.io/v1/restores namespaces: ignore: - null include: - allNote: The above configuration is for the Cluster-scoped installation of TVK. This includes all namespaces using labels, such as:
data.resource_config.yaml.resources[0].events.namespaces.include[0].allFor the namespace-scoped installation of TVK, you can include only the namespace where the TVK installation is present. -
After botkube-configmap is updated, it will start populating notifications for any operations performed on the TVK resources.
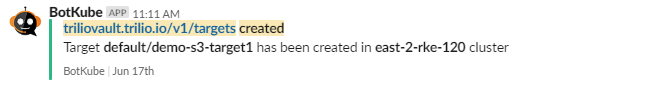
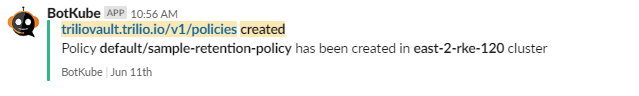
Configure TVK Resource Commands to execute from Slack
-
You can expand the list of commands that can be executed from Slack directly onto the Kubernetes resources and TVK resources.
kubectl edit configmap botkube-configmap -n botkube -
Add the commands that can be executed on the TVK resources along with the verbs, as shown in the sections below.
data.resource_config.yaml.settings.kubectl.commands.resources data.resource_config.yaml.settings.kubectl.commands.verbs# data: # resource_config.yaml: | # … settings: clustername: east-2-rke-120 configwatcher: true kubectl: enabled: true commands: resources: - deployments - pods - namespaces - daemonsets - statefulsets - storageclasses - nodes - licenses - policies - hooks - targets - backupplans - backups - restores - triliovaultmanagers verbs: - api-resources - api-versions - cluster-info - describe - diff - explain - get - logs - top - auth - create - get - edit - delete defaultNamespace: default - Once the botkube-configmap is updated, you’ll be able to see the updated commands list from Slack.
-
Users can also create a
resource_config.yamlfile with the configuration of resources and verbs from Step 2 of “Configure TrilioVault for Kubernetes Resource Monitoring” and Steps 2 of “Configure TVK Resource Commands to execute from Slack”. Users can then apply it while performing the BotKube installation. Pass the yaml file as a flat tohelm installcommand.$ helm install --version v0.12.1 --name botkube --namespace botkube -f /path/to/resource_config.yaml --set=...other args.. -
Once you apply the configuration during installation, you can also update the configuration by updating the configMap mentioned in the above steps. This will help you while performing the Helm upgrade of BotKube. Usage of Commands and Verbs
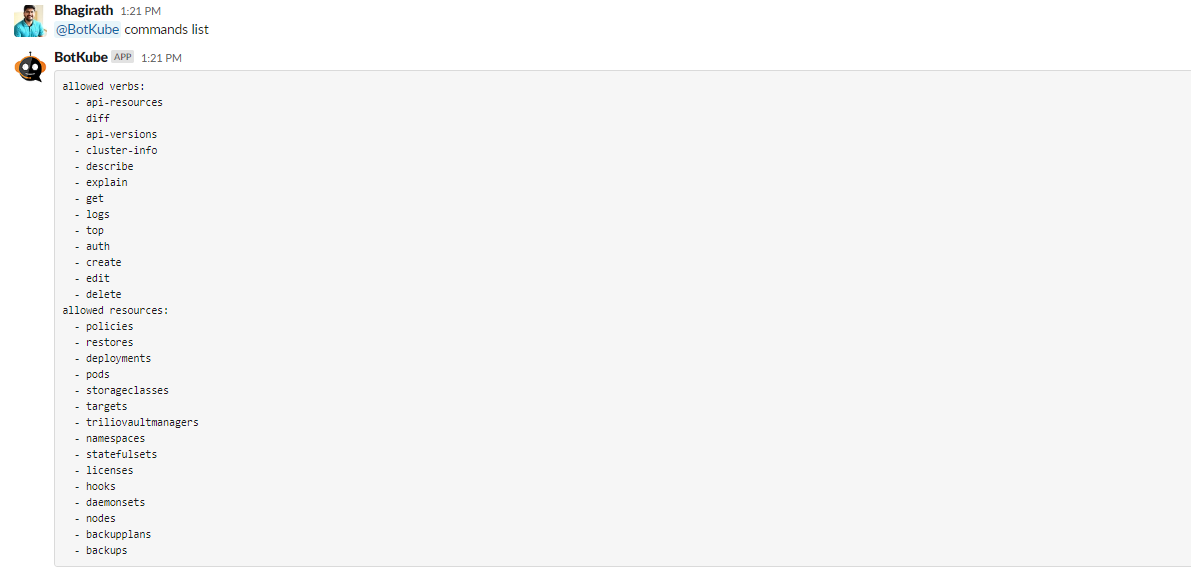
Usage of Commands and Verbs
You can execute the above commands directly from Slack to monitor the TVK resources.
-
Get
backupplansfrom all namespaces through Slack.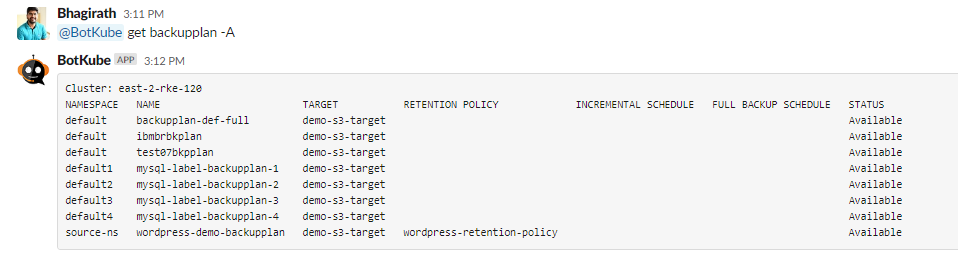
-
Get
backupsofdefaultnamespace through Slack.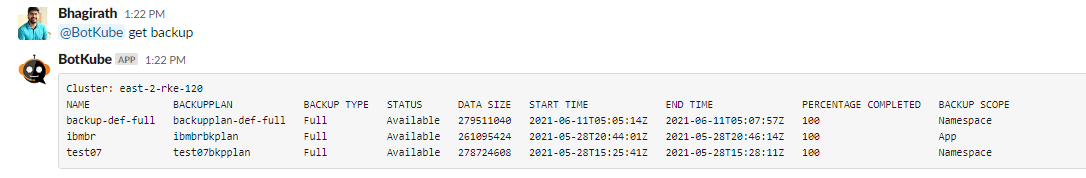
Perform a Backup/Restore Operation on a Sample Application Using TVK
Note: The steps below show resources deployed by a sample application and resources monitored by BotKube along with how the notifications look on Slack. All TVK resource yamls are located here.
-
Deploy a sample MySQL database application using Helm charts.
root@my-host:~# helm ls -n sourcens NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION mysql-qa sourcens 1 2021-07-20 10:08:06.476467405 +0000 UTC deployed mysql-1.6.9 5.7.30 root@my-host:~# kubectl get pods -n sourcens NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE mysql-qa-69f56f9966-cpj2f 1/1 Running 0 44h -
Create the backup target required to upload and store the backup metadata and volume data.
root@my-host:~# kubectl get target -n sourcens NAME TYPE THRESHOLD CAPACITY VENDOR STATUS BROWSING ENABLED demo-s3-target ObjectStore 100Gi AWS Available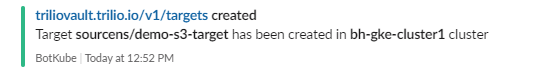
-
Create a hook for data consistency while performing the backup operation.
root@my-host:~# kubectl get hooks -n sourcens NAME AGE mysql-hook 45h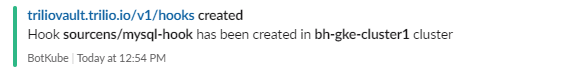
-
Create the backupplan required to perform the namespace backup sourcens.
root@my-host:~# kubectl get backupplan -n sourcens NAME TARGET RETENTION POLICY INCREMENTAL SCHEDULE FULL BACKUP SCHEDULE STATUS mysql-backupplan demo-s3-target Available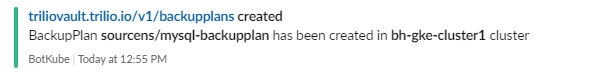
-
Now, we can perform the namespace backup of sourcens.
root@my-host:~# kubectl get backup -n sourcens NAME BACKUPPLAN BACKUP TYPE STATUS DATA SIZE START TIME END TIME PERCENTAGE COMPLETED BACKUP SCOPE mysql-hook-helm-full-backup mysql-backupplan Full Available 362151936 2021-07-20T16:28:22Z 2021-07-20T16:33:15Z 100 Namespace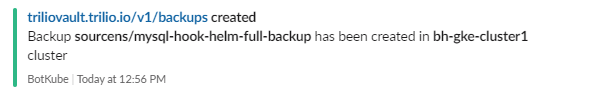
-
Since we already have a backup created and stored to the backup target location, use that same backup to perform a restore operation on a different namespace restorens.
root@my-host:~# kubectl get restore -n restorens NAME BACKUP BACKUP NAMESPACE STATUS DATA SIZE START TIME END TIME PERCENTAGE COMPLETED RESTORE SCOPE mysql-helm-restore mysql-hook-helm-full-backup sourcens Completed 219618872 2021-07-20T16:34:54Z 2021-07-20T16:37:59Z 100 Namespace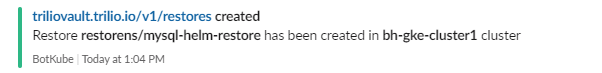
Remove BotKube from Kubernetes Cluster
Install the BotKube back-end using Helm and execute the command below to remove BotKube and its related resources completely.
helm delete --purge botkube -n botkube
Conclusion
Slack is one of the fastest growing communication tools leveraged by many organizations involved in cloud-native application development and delivery. InfraCloud’s BotKube simplifies the integration of Kubernetes applications into Slack. BotKube can also be configured with TVK for the same purpose. With BotKube, users can receive notifications and manage TVK from the communication tool they’re already using, adding another layer of convenience. Additional integrations with other communication tools (Mattermost, MFST Teams, etc.) are also available from BotKube.
This is a guest post written by Bhagirath Hapse, Solutions Engineer, Trilio
Looking for help with observability stack implementation and consulting? do check out how we’re helping startups & enterprises as an observability consulting services provider.
Stay updated with latest in AI and Cloud Native tech
We hate 😖 spam as much as you do! You're in a safe company.
Only delivering solid AI & cloud native content.